

System Characteristics
Chapter 5 Page 2
Normal System Operation

System Factors to consider when looking for Sealed System Performance
Before entering the sealed system there are certain factors both mechanical and electrical which can affect cooling. A technician should first check this first.
It is recommended to familiarize yourself with refrigerators that are working normally first to be able to compare your findings of refrigerators that are not cooling with the conditions of ones that are working.
When testing the refrigerator to determine if it is a sealed system or other factor these eight tests should be made first and recommend the tests be made in the following order.
1. Fresh Food Temperature
2. Freezer Temperature
3. Average Amps and Wattage draw of the compressor - Note this works with standard compressors
4. Condenser discharge line temperature
5. Condenser temperature
6. Frost Pattern
7. Low Side Pressure
8. High Side Pressure
Air movement- All fans must be operational. If static condenser is used, there must be sufficient air space around the condenser to allow for convection cooling. Forced air condensers need to be vacuumed from time to time to prevent lint, cat hair, dog hair, etc. from plugging the coil and reducing cooling capacity
More: Proper air flow. Since most new refrigerators use tube and fin evaporators and forced air condensers, fan operation is critical. If the evaporator fan stops, heat transfer ceases and the freezer temperature rise. Likewise, a condenser fan failure inhibits the condensers' ability to release its heat and cooling capacity is severely diminished.
The system reaction to the lack of air movement depends on which of the fan motors fails.
Evaporator fan: Since the refrigerant is not absorbing heat, system pressures drop. Lower pressures mean that the compressor does not have to work as hard and current draw is reduced. Note: Failure of one of the defrost system components will have the same effect as the evaporator fan stopping. If the frost is not removed regularly from the evaporator, the frost turns into and ice which eventually plugs the fins of the coil. Air movement through the coil stops. Additionally, the ice acts as an insulator, further reducing the transfer of heat to the refrigerant. Just as with a stopped evaporator fan, system pressures and current draw decrease with a plugged evaporator.
Condenser fan: System pressures increase since the refrigerant is not able to release its heat. Higher pressure means the compressor has to work harder and current draws increases. If the compressor gets hot enough, the overload may open the run circuit to the compressor and stop all cooling. Note: A condenser that is plugged with dog or cat hair will have much the same effect on sealed system performance as a stopped condenser fan motor.
Ambient Temperatures. High ambient temperatures (the temperature of the air that surrounds the exterior of the refrigerator) place an undue strain on any sealed system. Some of the negative effects are:
Uses more energy- Warmer air holds more moisture. Every time the customer opens either of the compartment doors, the cool dry air inside the refrigerator drops to the floor and is replaced with warm moist air. Not only does the system have to drop the sensible temperature of the air but a great deal of energy is used to remove the latent heat that is trapped in the moisture.
The air blowing across the condenser is warmer. This reduces the temperature differential between the condenser and the air and reduces the ability of the refrigerant to give up its heat.
Pressures increase. The added heat load, in combination with the warmer condenser temperatures, increases both the low and high side pressures. Higher pressures mean that the boiling and condensing points of the refrigerant are raised. Not only is the refrigerant’s ability to absorb heat reduced but the higher condenser temperature makes it more difficult for the refrigerant to release its heat.
Compressor works harder. Greater heat load in conjunction with higher pressures cause the compressor to draw more current.
Below are examples of problems which may look like a Sealed System but may be something else.
1. Plugged Condenser - This is when the air flow over the condenser is blocked in some way, Such as, Pet hair, paper towel, back cover removed from compressor area. If the air is not able to flow over the condenser properly it will not to be able to release the heat from the refrigerant.
Here are the symptoms of a plugged condenser.

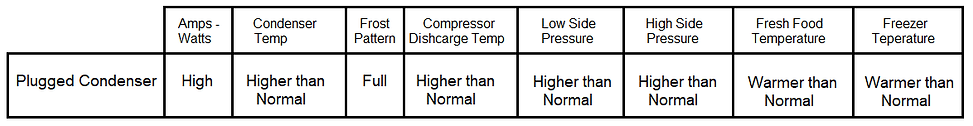
2. Blocked Condenser Fan- This is when the air flow over the condenser fan is blocked in some way insulation, rodent, or other debris may get pulled into the fan by the air flow. This can get caught in the fan blade and stop it from turning. A defective fan motor could also cause this. If the air is not able to flow over the condenser properly it will not to be able to release the heat from the refrigerant.
Here are the symptoms of a blocked condenser fan.

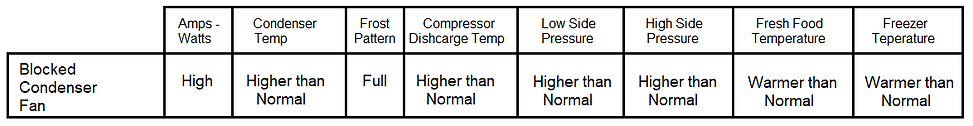
3 High Heat Load - This is when the air inside the refrigerator is hotter than normal.
1. Unit was open for cleaning or door was not properly closed
2. Refrigerator light stays on and does not turn off
3. Defrost heater is operating during cooling cycle
4. Ice maker mold heater on
5. Dispenser door flap not closing
Here are the symptoms of a High Heat Load.

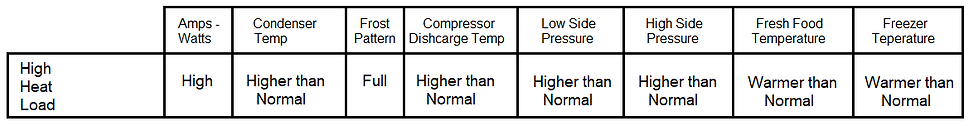
4 High Ambient - This is when the air outside the refrigerator is affecting how well the condenser releases refrigerant heat and how well the refrigerator is insulated..
1. Unit is in a garage
2. Next to a heating source Ex. stove, external heater
3. Condenser is a static condenser and exposed to direct sunlight or too close to the walls
4. Warm wall condenser exposed to direct sunlight or too close to the walls or in a garage
Here are the symptoms of a High Ambient.


5 Blocked evaporator fan- This is when the fan inside the refrigerator is bad or the blades have an obstruction not allowing it to turn. This will reduce the amount of heat the evaporator could absorb.
1. Bad fan motor or bearings
2. Ice obstruction blocking fan rotation
3. Wire blocking fan rotation
Here are the symptoms of a Blocked Evaporator fan.


6 Iced Up Evaporator - This is when the fan inside the refrigerator is unable to pull the heat across the evaporator, this will reduce the amount of heat the evaporator could absorb.
1. Refrigerator is not defrosting
2. Ice obstruction in evaporator drain line
3. Ice maker fill tube leaking onto evaporator
Here are the symptoms of an Iced Evaporator.


7 Damper Failed Closed - The damper goes between the freezer and refrigerator. Almost all evaporators when they close do not close 100% this varies with different models. If the damper were to fail in the closed position this would keep a majority of the air inside the freezer therefore the refrigerator may be cool but not cold enough and the freezer would be colder than normal.
Here are the symptoms of Damper failed Closed.


8 Damper Failed Open - The damper goes between the freezer and refrigerator. Almost all evaporators when they close do not close 100% this varies with different models. If the damper were to fail in the open position this would force freezer air into the refrigerator and possible cause excessive freezing inside the refrigerator compartment, and cause the freezer to be warmer than normal.
Here are the symptoms of Damper failed Closed.

